
, pupillary, stretch and vestibulo-ocular reflexes. Observe the reaction of the patient's pupils to light directed in the left or right eye. ThePupillary Light Reflex Pathway begins with the photosensitive retinal ganglion cells, which convey information to the optic nerve (via the optic disc). The cranial nerves involved in the eye blink response and pupillary response are the optic, oculomotor, trigeminal and facial nerves. The iris sphincter is controlled by the parasympathetic system, whereas the iris dilator is controlled by the sympathetic system. Which of the following cranial nerve mediates the corneal reflex? In this setting, it is very unlikely that left consensual reflex, which requires an intact segment 4, would be preserved. Nerve impulses pass along the optic nerve, to the co-ordinating cells within the midbrain. Although IV atropine given within 30 minutes of surgery is believed to reduce incidence, it is no longer recommended for routine prophylaxis. away) object to a nearby object (Nolte, Figure 17-40, Pg. The accommodation response is elicited when the viewer directs his eyes from a distant (greater than 30 ft. This action involves the contraction of the medial rectus muscles of the two eyes and relaxation of the lateral rectus muscles. Pathway: Afferent signals are from the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve.

Adies tonic pupil syndrome is a relatively common, idiopathic condition caused by an acute postganglionic neuron denervation followed by appropriate and inappropriate reinnervation of the ciliary body and iris sphincter. Observation: You observe that the patient has normal vision but that his pupils, You conclude that his eye's functional loss is, Pathway(s) affected: You conclude that structure(s) in the, Side & Level of damage: As the pupillary response deficit. (dilation of the pupil with light touch to the back of the neck. Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors. The contralateral efferent limb causes consensual light reflex of the contralateral pupil. The accommodation neural circuit: The circuitry of the accommodation response is more complex than that of the pupillary light reflex (Figure 7.6). Pathway: The trigeminal nerve or cervical pain fibers, which are part of the lateral spinothalamic tract, carry the afferent inputs of the ciliospinal reflex.

This page was last edited on 7 January 2023, at 06:24. The oculocardiac reflex is a dysrhythmic physiological response to physical stimulation of the eye or adnexa specifically, it is defined by a 1020% decrease in the resting heart rate and/or the occurrence of any arrhythmia induced by traction or entrapment of the extraocular muscles and/or pressure on the eyeball sustained for at least 5 seconds.
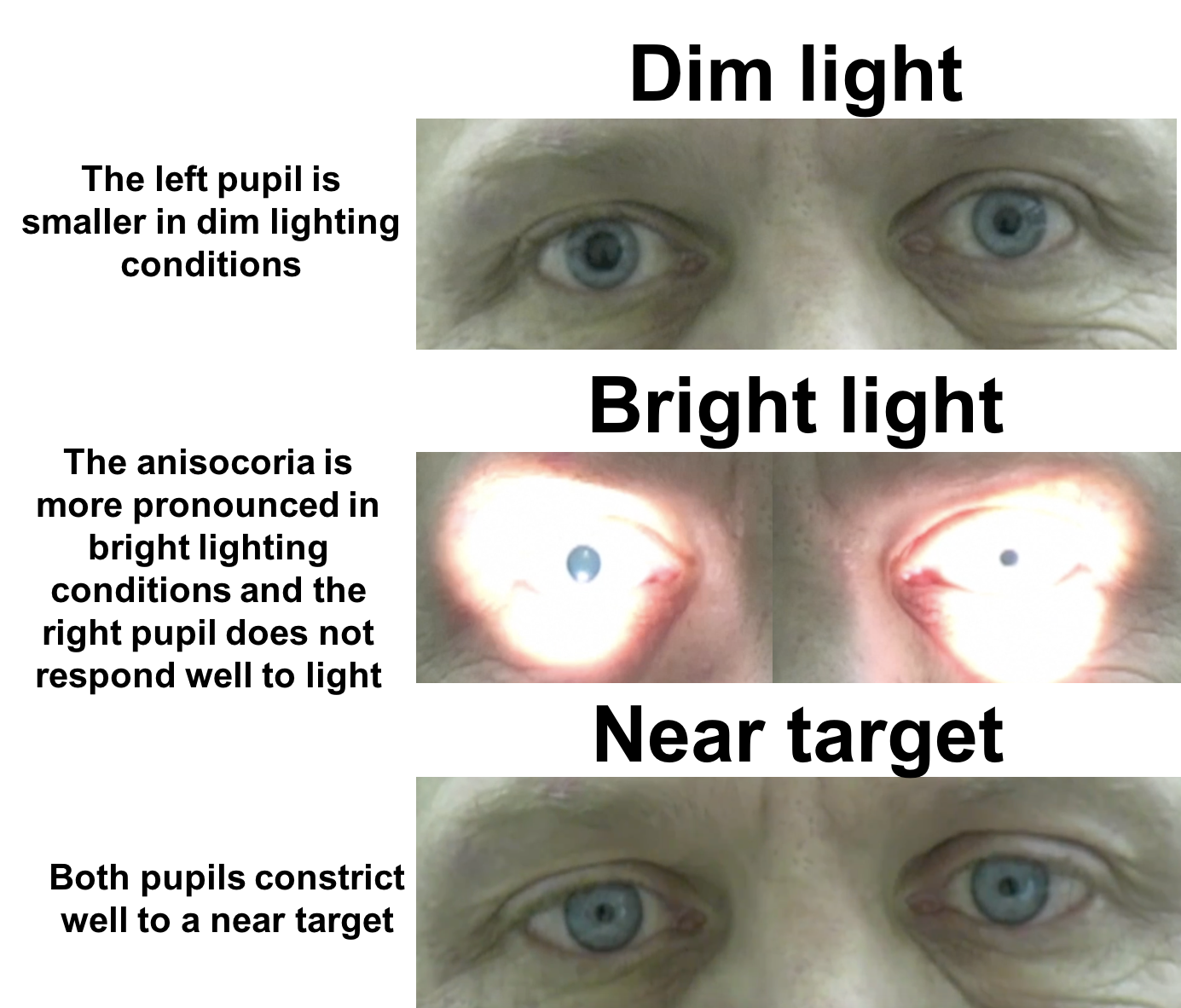
The pupillary light reflex pathway involves the optic nerve and the oculomotor nerve and nuclei. Each efferent limb has nerve fibers running along the oculomotor nerve (CN III). The direct response is the change in pupil size in the eye to which the light is directed (e.g., if the light is shone in the right eye, the right pupil constricts). Emergency physicians routinely test pupillary light reflex to assess brain stem function. Direct and consensual responses should be compared in the reactive pupil. Tactile stimulation of the cornea results in an irritating sensation that normally evokes eyelid closure (an eye blink). Five basic components of the pupillary light reflex pathway


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
